Wood lathe tools are essential instruments in the craft of woodturning, a discipline that involves shaping and finishing wood pieces through rotation on a lathe. These tools are specifically designed to carve, cut, and refine wood into various forms and textures, ranging from simple cylindrical shapes to intricate artistic designs. The primary purpose of wood lathe tools is to transform raw wood into functional or decorative objects, such as bowls, spindles, and furniture components.
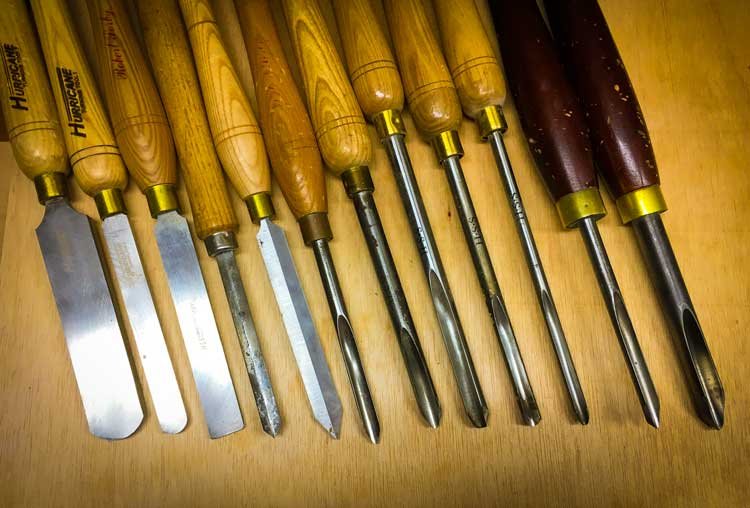

In the woodworking process, wood lathe tools play a crucial role in both the initial shaping and the final finishing stages. The assortment of tools includes gouges, chisels, parting tools, and scrapers, each serving a distinct function. For example, gouges are typically used for roughing out and shaping, while chisels assist in creating smooth, detailed cuts. Parting tools help in making precise cuts to separate sections of the wood, and scrapers are ideal for achieving a fine finish.
The versatility of wood lathe tools enables woodturners to experiment with various techniques to create unique textures and patterns. Whether it’s hollowing out a bowl or adding decorative details to a spindle, the options are virtually limitless. By mastering the use of these tools, woodturners can produce a wide array of products, from practical household items to elaborate artistic pieces.
Overall, wood lathe tools are indispensable for anyone involved in woodturning. Their ability to manipulate wood into diverse shapes and finishes makes them a fundamental aspect of the craft. Understanding the purpose and application of each tool is essential for achieving desired results in any woodworking project.
Types of Wood Lathe Tools
Wood lathe tools come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each designed for specific tasks in the woodturning process. Understanding these tools and their applications is crucial for achieving precision and artistry in your projects.
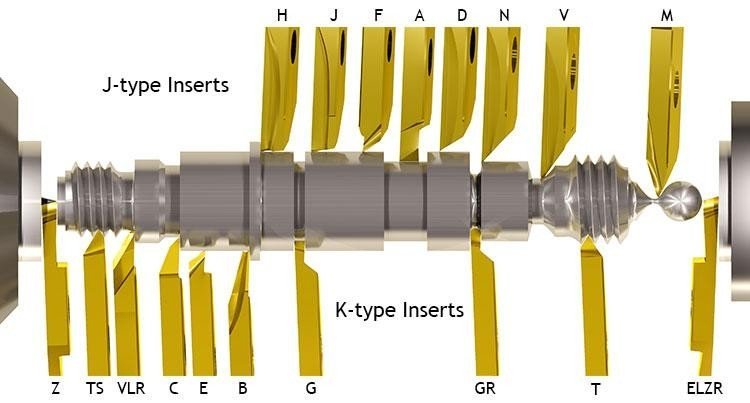
Gouges are among the most versatile wood lathe tools. There are three primary types: bowl gouges, spindle gouges, and detail gouges. Bowl gouges have a deep, U-shaped flute and are ideal for hollowing out bowls. Spindle gouges feature a shallower flute, making them perfect for turning wooden spindles and other long, thin objects. Detail gouges, with their pointed tips, are used for intricate designs and fine detail work.
Skews are another essential type of wood lathe tool. These tools have a flat, angled blade, which allows for smooth cuts and a fine finish on spindle work. They are particularly useful for planing and cutting sharp edges, making them indispensable for achieving clean, precise results.
Parting tools, as their name suggests, are used to part off sections of wood. These tools have a narrow blade designed to cut deep and separate parts of the workpiece. They are also useful for creating grooves and tenons.
Scrapers are flat-bladed tools used for refining shapes and smoothing surfaces. They come in various shapes, such as round, square, and triangular, each suited for different tasks. Scrapers are especially beneficial when working with difficult grain patterns or achieving a smooth surface on end grain.
In addition to these fundamental tools, there are specialty tools designed for more specific tasks. Hollowing tools, for example, are used to create deep, hollow forms within a workpiece. Chatter tools produce decorative patterns by vibrating against the wood, while texturing tools add unique surface finishes. These specialized tools expand the creative possibilities in woodturning, allowing for more intricate and expressive designs.
Tool Materials and Characteristics
When selecting wood lathe tools, the material from which they are crafted plays a pivotal role in performance and durability. Predominantly, wood lathe tools are made from high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and carbon steel. Each material offers unique benefits and considerations, influencing the choice based on specific woodturning needs.
High-speed steel (HSS) is widely favored among woodturners due to its excellent balance of affordability, durability, and ease of sharpening. HSS tools maintain their edge well and can be honed to a fine sharpness, making them suitable for intricate and detailed work. Moreover, HSS tools are resilient to the high temperatures generated during woodturning, reducing the risk of edge softening.
Carbide tools, on the other hand, are renowned for their exceptional hardness and longevity. These tools are equipped with carbide inserts that can be rotated to expose fresh cutting edges, significantly extending their useful life. While carbide tools tend to be more expensive, their ability to maintain a sharp edge with minimal maintenance makes them an attractive option for both novice and professional woodturners. However, they may not achieve the same level of sharpness as HSS tools, making them less ideal for extremely fine detail work.
Carbon steel tools, although less common today, are still appreciated by some traditional woodturners. These tools are typically more affordable and can be sharpened to a very keen edge. However, carbon steel is more prone to wear and requires frequent sharpening, which can interrupt the workflow. Additionally, carbon steel tools are more susceptible to rust, necessitating careful maintenance to ensure longevity.
Beyond the blade material, the importance of ergonomic handles cannot be overstated. The handle design and material significantly impact the comfort and control a woodturner experiences. Ergonomically designed handles reduce hand fatigue and provide better grip, allowing for more precise and controlled tool movements. Consideration of handle length, weight, and grip material is essential for enhancing the overall woodturning experience.
Techniques for Using Wood Lathe Tools
Mastering the art of woodturning requires a fundamental understanding of various techniques used with wood lathe tools. This guide begins with the basics and progresses to more advanced methods, ensuring that both novice and experienced woodturners find value.
One of the first techniques to master is roughing. Using a roughing gouge, woodturners shape the raw material into a balanced and cylindrical form. This foundational step sets the stage for more detailed work. With a firm grip and steady pressure, the roughing gouge efficiently removes excess material, preparing the wood for finer detailing.
Next, shaping involves the use of spindle gouges and skew chisels to define the desired form. Whether crafting a bowl or a spindle, shaping demands precision and control. By gradually removing material and refining the contours, woodturners achieve the intended design. The skew chisel, in particular, is excellent for creating smooth surfaces and sharp lines, adding a professional touch to the piece.
Finishing is the final step in basic woodturning techniques. Employing a scraper or parting tool, woodturners smooth out any roughness and achieve the desired texture. Sandpaper of varying grits is often used to further polish the surface. Proper finishing not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also prolongs the life of the wood piece.
Advanced woodturning techniques such as hollowing, threading, and segmented turning open up new creative possibilities. Hollowing, using specialized hollowing tools, allows for the creation of vessels with narrow openings and thin walls. Threading tools enable the addition of intricate screw threads, perfect for lidded containers. Segmented turning involves assembling and turning multiple pieces of wood into a single, cohesive design, showcasing complex patterns and contrasts.
To achieve intricate designs and details, it is crucial to maintain sharp wood lathe tools and employ a steady hand. Patience and practice are key, as is a thorough understanding of the wood’s grain and characteristics. By combining these techniques and constantly refining their skills, woodturners can master the use of wood lathe tools and create exceptional pieces.
Selecting the Right Wood Lathe Tools
Choosing the right wood lathe tools is a crucial step in ensuring the success of your woodturning projects. Several factors must be considered to make an informed decision. Firstly, the type of wood species you are working with plays a significant role. Hardwoods like oak and maple require sturdier, sharper tools, while softer woods such as pine or cedar can be managed with less robust instruments. The hardness of the wood influences the wear and tear on your tools, necessitating frequent sharpening or even replacement.
Another essential factor is the desired surface finish. For projects requiring a smooth, fine finish, tools with sharper angles and finer edges are preferred. On the other hand, roughing out blanks or initial shaping can be accomplished with heavier, more robust tools. The thickness of the wood and the intricacy of the design also determine the choice of tools. For intricate detailing, smaller, more precise tools are required, whereas larger tools are suitable for bulk material removal.
Specific project requirements also guide tool selection. For instance, turning bowls often necessitates a bowl gouge, which has a deeper flute and can handle the curvatures of bowl interiors. Spindle turning, on the other hand, benefits from tools like spindle gouges and skew chisels, which provide control and precision for long, cylindrical shapes. For pen turning, smaller and more detailed tools such as parting tools and small gouges offer the precision needed for such fine work. (CNC Tune for Instagram)
When selecting wood lathe tools, considering the size and shape of the tools is essential. Bowl gouges typically come in sizes ranging from 1/4 inch to 3/4 inch, each size catering to different stages of bowl turning. Spindle gouges also vary in size, with 3/8 inch and 1/2 inch being common choices for general spindle work. Pen turning tools are typically smaller, with sizes around 1/8 inch to 1/4 inch, suited for the delicate nature of pen blanks.
By carefully evaluating these factors, woodturners can select the most appropriate wood lathe tools for their projects, ensuring both efficiency and quality in their craftsmanship.
Maintenance and Care of Wood Lathe Tools
Proper maintenance and care of wood lathe tools are crucial for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. Cleaning your tools after each use is a fundamental practice. Begin by wiping down the tools with a clean, dry cloth to remove sawdust and debris. For more stubborn residue, a brush or compressed air can be employed. It’s essential to avoid using water as it can lead to rust formation. Instead, consider using a light coat of oil to protect the metal surfaces.
Sharpening is another critical aspect of maintaining wood lathe tools. Dull tools not only reduce efficiency but also compromise the quality of your work. Utilize a sharpening stone or a grinding wheel to restore the cutting edge of your tools. It’s important to maintain the original bevel angle of the tool while sharpening. Frequent, light sharpening is preferable to infrequent, heavy sharpening, as the latter can remove more material than necessary and shorten the tool’s lifespan.
Storing your wood lathe tools properly can prevent rust and damage. Ideally, tools should be stored in a dry, cool environment. Using a tool rack or a dedicated storage cabinet can keep them organized and protected. Ensure that the storage area is free from moisture to prevent rust. Applying a thin layer of oil before storage can also help in rust prevention. Additionally, using protective covers or cases can shield the tools from dust and accidental impacts.
By following these maintenance and care practices, woodturners can ensure that their wood lathe tools remain in excellent condition, providing consistent and reliable performance. Regular cleaning, diligent sharpening, and thoughtful storage are the cornerstones of effective tool maintenance, contributing to the overall quality of woodturning projects.
Common Issues in Woodturning and Troubleshooting
Woodturning, while immensely rewarding, is not without its challenges. One of the most frequent issues encountered involves the maintenance of wood lathe tools. Dull edges on these tools can lead to suboptimal performance and increased effort. To address this, regular sharpening is imperative. Using a sharpening jig can ensure consistent angles and maintain the precision of your tools. Additionally, honing the tools with a leather strop can help achieve a razor-sharp edge, reducing the risk of tearout.
Another prevalent problem is wood cracking. This typically occurs due to rapid moisture loss or uneven drying. To mitigate this, it is essential to use properly seasoned wood and to control the drying process by sealing the ends with wax or using a slower drying method. If cracks do appear, they can often be repaired with wood fillers or by incorporating design elements such as inlays or decorative features.
Tearout, where fibers are torn from the wood surface, is another common issue. This can result from using improperly sharpened tools or from turning against the grain. To minimize tearout, ensure your wood lathe tools are sharp and take light, controlled cuts. Additionally, cutting with the grain, rather than against it, can significantly reduce the likelihood of this problem. For existing tearout, sanding with progressively finer grits can help smooth the surface.
Other frequent woodturning problems include vibration and tool chatter. These issues can be caused by improper tool rest positioning, imbalanced wood blanks, or excessive lathe speed. Properly securing the wood blank, adjusting the tool rest to the correct height and distance, and selecting an appropriate speed for the material being turned can help alleviate these issues. Ensuring the lathe itself is stable and on a level surface is also critical.
By understanding and addressing these common issues, woodturners can achieve more consistent results and enjoy a more satisfying woodturning experience. Regular maintenance of wood lathe tools and adopting proper techniques can go a long way in minimizing problems and enhancing the quality of the finished product.
Safety Considerations When Using Wood Lathe Tools
Ensuring safety while working with wood lathe tools is paramount. The use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is a crucial first step in safeguarding oneself against potential hazards. Woodturners should always don face shields to protect against flying debris and dust masks to prevent inhalation of fine particles. Additionally, hearing protection is recommended to mitigate the risk of hearing damage from prolonged exposure to high decibel levels produced by wood lathe machinery.
Establishing a safe setup for wood lathe operations is another vital consideration. The work area should be well-lit and free of clutter, with all tools and materials organized and within easy reach. It is essential to secure the wood lathe on a stable surface to prevent any movement during use. Before starting the lathe, woodturners should verify that all components, including the tool rest and tailstock, are properly tightened. Regular maintenance checks on the lathe and tools can prevent unexpected malfunctions that could lead to accidents.
Operating the wood lathe with caution is equally important. Always use sharp tools, as dull blades can cause the tool to catch and potentially lead to injury. Woodturners should maintain a balanced stance and keep their hands and body clear of the rotating wood. Never wear loose clothing or jewelry that could get caught in the lathe. It is advisable to start the lathe at a low speed and gradually increase it to the desired level, ensuring control over the tool and workpiece.
In the event of an accident or tool mishap, having a well-defined emergency procedure is essential. Immediate steps should include turning off the lathe and assessing the situation. If there is a minor injury, basic first aid should be administered. For more severe injuries, it is crucial to seek professional medical assistance without delay. Maintaining a first aid kit and emergency contact numbers in the workshop can significantly enhance response times during such incidents.
Advantages of Using Wood Lathe Tools
Wood lathe tools provide an unparalleled level of precision and control, enabling woodturners to achieve exact shapes and intricate contours. The precise nature of these tools makes them indispensable for craftsmen aiming for meticulous detail and uniformity in their projects. Whether you’re crafting the delicate curves of a bowl or the straight lines of furniture components, wood lathe tools ensure a level of accuracy that is difficult to achieve with other woodworking equipment.
The versatility of wood lathe tools is another significant advantage. These tools can be used to create an extensive range of projects, from simple spindles to complex, multi-faceted designs. Whether you are working on small decorative items like pens and ornaments or larger pieces such as table legs and chair spindles, the adaptability of wood lathe tools makes them essential in any woodturner’s arsenal.
Additionally, wood lathe tools open up vast opportunities for artistic expression and customization. The ability to manipulate wood into virtually any shape allows artisans to infuse their work with unique, personalized touches. This creative freedom is crucial for those looking to push the boundaries of traditional woodworking, creating pieces that are not only functional but also visually striking. The customizability provided by wood lathe tools ensures that each project can be tailored to meet specific aesthetic and functional requirements, making it possible for woodturners to produce truly one-of-a-kind works of art.
In summary, the advantages of using wood lathe tools are manifold. They offer precision and control that are essential for achieving exact shapes and contours, demonstrate remarkable versatility in the range of projects they can handle, and provide ample opportunities for artistic expression and customization. These benefits make wood lathe tools an invaluable asset for both novice and experienced woodturners alike.
Innovations and Trends in Wood Lathe Tools
Recent years have seen significant advancements in the design and functionality of wood lathe tools, enhancing both efficiency and performance for woodturners. One notable innovation is the development of ergonomic tool handles, which are designed to reduce user fatigue and provide better control. These handles often feature non-slip grips and are made from durable materials that withstand extensive use. Additionally, high-speed steel (HSS) and carbide-tipped tools have become increasingly popular due to their superior edge retention and reduced need for frequent sharpening.
Technology integration has further revolutionized wood lathe tools. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems have made precise, automated woodturning possible, allowing for intricate designs and repeatable patterns that were once incredibly time-consuming to achieve by hand. CNC tools enable woodturners to produce complex shapes with high precision, significantly speeding up the production process. Similarly, laser guidance systems have been introduced to assist in achieving exact dimensions and symmetrical designs. These laser systems project a beam onto the workpiece, serving as a visual guide for cutting and shaping, thus minimizing errors and enhancing accuracy.
Looking ahead, the future of wood lathe tools appears promising with continued advancements in materials and technology. One anticipated trend is the further integration of smart technology, such as sensors that monitor tool wear and performance in real-time. These sensors could provide feedback to the woodturner, indicating when a tool needs maintenance or replacement, thereby optimizing workflow and extending tool life. Moreover, advancements in material science may lead to the development of even more durable and efficient cutting materials, reducing the environmental impact and cost of frequent replacements.
In summary, the evolution of wood lathe tools is characterized by a blend of ergonomic design, advanced materials, and cutting-edge technology. These innovations not only enhance the woodturning experience but also pave the way for more efficient, precise, and sustainable woodworking practices. As these trends continue to develop, woodturners can look forward to even greater advancements that will elevate their craft to new heights.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have delved into the essential aspects of wood lathe tools, exploring their varied benefits and applications. Wood lathe tools are indispensable for woodturners, enabling the creation of intricate designs and functional pieces with precision and ease. From the selection of the appropriate wood lathe tools to mastering their use, each step is crucial in achieving high-quality results.
We examined the fundamental types of wood lathe tools, including gouges, chisels, and parting tools, highlighting their specific uses and advantages. Understanding the unique characteristics and purposes of these tools allows woodturners to enhance their craftsmanship and expand their creative possibilities. Additionally, we discussed the importance of proper maintenance and sharpening techniques to ensure the longevity and optimal performance of wood lathe tools.
As the field of woodworking continues to evolve, significant advancements in wood lathe tool technology are anticipated. Innovations such as enhanced materials, ergonomic designs, and digital integrations are likely to revolutionize the way woodturners approach their craft. For instance, the development of smart wood lathe tools equipped with sensors and real-time feedback mechanisms could offer unprecedented precision and control, further elevating the art of woodturning.
Moreover, sustainable practices and eco-friendly materials are gaining traction within the woodworking community. Future trends may see an increased focus on environmentally conscious wood lathe tools, promoting both the art and the responsibility of woodworking. As these advancements unfold, woodturners must stay informed and adapt to new techniques and tools, ensuring they remain at the forefront of their craft.
Ultimately, the mastery of wood lathe tools is a continuous journey of learning and adaptation. By embracing the evolving landscape of woodturning technology and practices, woodturners can look forward to a future filled with innovative opportunities and creative achievements.
Additional Resources and References
For those keen on delving deeper into the world of wood lathe tools and woodworking techniques, a wealth of resources is available. Books such as “Woodturning: A Foundation Course” by Keith Rowley and “The Lathe Book: A Complete Guide to the Machine and Its Accessories” by Ernie Conover are excellent starting points. These texts provide comprehensive guides, covering everything from basic wood lathe tool techniques to advanced woodturning projects.
Online articles and websites also offer a treasure trove of information. The American Association of Woodturners (AAW) website is a valuable resource, featuring articles, tutorials, and forums where woodturners can exchange ideas and advice. Additionally, websites like Woodturning Online and The Woodworkers Institute host numerous articles and video tutorials that can help both beginners and seasoned woodworkers refine their skills with wood lathe tools.
For those looking to gain hands-on experience, several courses and workshops are available. Renowned institutions such as The Woodworkers Guild of America and the Marc Adams School of Woodworking offer courses tailored to various skill levels. These programs cover a range of topics, from basic wood lathe tool usage to intricate woodturning techniques.
Certifications can also be a valuable asset for those wishing to formalize their expertise. The AAW provides a certification program that recognizes advanced skills in woodturning and the safe use of wood lathe tools. This certification can not only enhance your credibility but also open up opportunities for teaching and professional growth.
In addition to these resources, local woodworking clubs and community centers often host workshops and meetups. These events provide opportunities for practical learning and networking with fellow enthusiasts, fostering a collaborative environment where skills and knowledge about wood lathe tools can be shared and expanded.

Leave a Comment