In an era where precision and efficiency are paramount in fabrication and manufacturing, the mini CNC lathe machine emerges as a revolutionary tool for beginners and seasoned professionals alike. This compact powerhouse facilitates the creation of intricate designs with unparalleled accuracy, making it indispensable in small-scale production and personal projects. Understanding the intricacies of a mini CNC lathe machine is the first step towards harnessing its full potential, marking the importance of familiarizing oneself with its functionality, advantages, and applications. As we delve into a comprehensive exploration of this remarkable tool, our goal is to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of CNC machining and to achieve precision in your craftsmanship.

Our detailed guide will walk you through the basics of a mini CNC lathe machine, from choosing the right model for your specific needs to setting it up and understanding its control panel. We’ll also cover how to properly load and secure your workpiece, program the machine for precise operations, and explore advanced machining techniques that will elevate your projects. Furthermore, troubleshooting and maintenance tips will ensure your mini CNC lathe machine continues to perform with high efficiency, extending its lifespan and enhancing your machining experience. Join us as we unlock the capabilities of the mini CNC lathe machine, paving the way for innovation and excellence in your creations.
Understanding the Basics of a Mini CNC Lathe
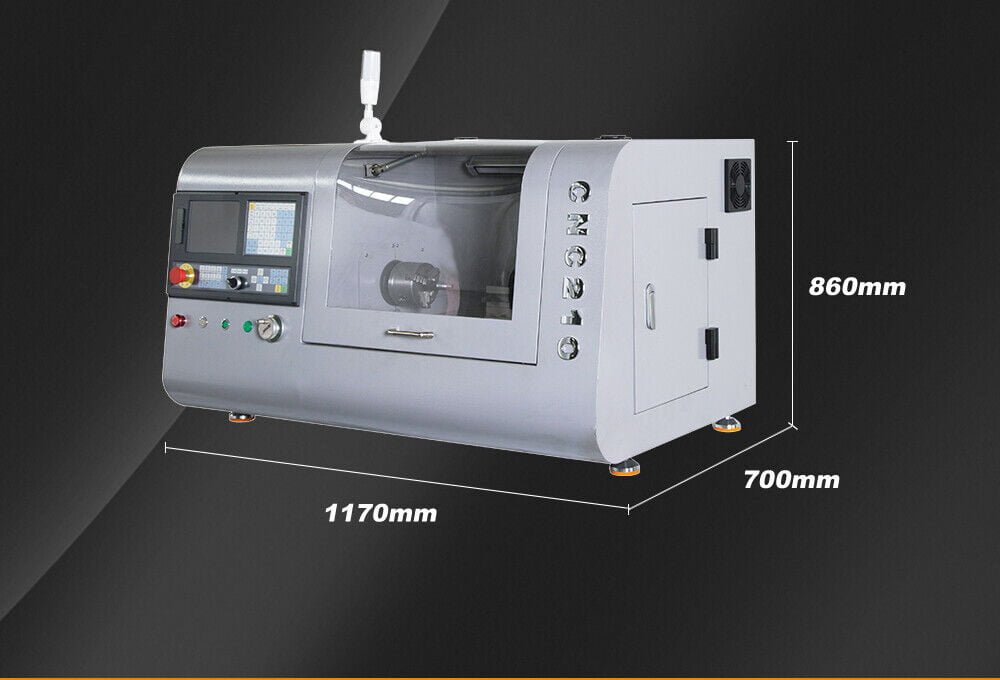
A mini CNC lathe is a compact and versatile tool that revolutionizes the way we approach small-scale machining projects. Its design is a scaled-down version of traditional CNC lathes, making it ideal for placement on a benchtop or desktop. This section will explore the fundamental aspects of mini CNC lathes, including their design, functionality, and the advantages they offer to both hobbyists and professional machinists.
What is a Mini CNC Lathe?
A mini CNC lathe incorporates advanced Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology to automate machining operations. Unlike larger industrial models, these mini lathes are designed to handle smaller projects with high precision. The core of CNC machining lies in its ability to control machine tools via pre-programmed software. This automation not only ensures accuracy but also significantly enhances the speed of manufacturing processes.
Key Features and Capabilities
Mini CNC lathes bring the capabilities of larger lathes into a more compact form. This feature is particularly beneficial for users with limited space, such as those working from home workshops or small businesses. Despite their size, these machines do not compromise on functionality. They can perform a wide range of machining tasks including turning, cutting, and drilling with precision that rivals larger machines.
- Precision and Control: The use of CNC technology allows for extremely precise machining. The computer-controlled setup ensures that each part is machined exactly to specification, which is crucial for applications requiring high precision.
- Versatility: Whether it’s metal, plastic, or wood, a mini CNC lathe can handle various materials. This versatility makes it an invaluable tool for anyone involved in multi-material crafting.
- Ease of Use: For beginners, the transition to CNC machining can be daunting. However, mini CNC lathes are generally easier to learn and operate, thanks to their user-friendly design and control software.
Advantages of Using a Mini CNC Lathe
The adoption of a mini CNC lathe in your machining process offers several benefits:
- Cost-Effective: Mini CNC lathes are generally more affordable than their larger counterparts, making them a great option for individuals or small businesses on a budget.
- Efficiency: With CNC automation, tasks that would typically take hours can be completed in a fraction of the time, increasing overall productivity.
- Customization: The precision of CNC machining allows for high customization of parts. Whether for unique projects or small batch production, these machines can deliver tailored results with consistency.
Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation for anyone interested in exploring the capabilities of mini CNC lathes. By leveraging their compact size and precision, users can enhance their machining projects, pushing the boundaries of what can be created in a small workshop setting.
Choosing the Right Mini CNC Lathe for Your Needs
When selecting the ideal mini CNC lathe for your needs, it’s crucial to consider several factors that align with the specific projects you plan to undertake. The choice of your mini CNC lathe should be based on the materials you intend to machine and the types of operations you wish to perform. Here, we’ll explore the key considerations and features to look for, as well as some popular models and brands that may suit your requirements.
Key Considerations and Features
- Project Requirements and Materials: Initially, determine the nature of your projects and the materials you will be working with. Different lathes have varied capabilities; for instance, some might be better suited for metals, while others may handle plastics or wood more efficiently.
- Size and Weight: If your workspace is limited or you anticipate needing to move the machine frequently, opt for a mini CNC lathe that is compact and lightweight. This makes it easier to fit into smaller spaces and relocate when necessary.
- Bed Length: The bed length of the lathe determines the maximum length of the workpiece you can accommodate. Ensure the bed length meets the requirements of your projects to avoid any limitations on the size of the workpieces you can machine.
- Spindle Speed: The spindle speed is crucial as it affects the effectiveness of machining different materials. Look for a lathe that offers adjustable speed settings to provide flexibility and precision in various machining tasks.
- Tooling Options: Verify if the lathe supports various tooling options. This flexibility allows you to undertake a broader range of machining operations and achieve more intricate designs.
- Control System: An intuitive control panel and user-friendly software are essential, especially for beginners. These features simplify the programming and operation of the lathe, making your machining process more efficient and less prone to errors.
Popular Models and Brands
When considering the purchase of a mini CNC lathe, exploring popular models and brands can help you make an informed decision. Here are a few recommendations:
- Tormach 8L Lathe: Known for its precision and compact design, the Tormach 8L is ideal for small workshops and offers features like diverse material handling and operation on standard 120VAC. It supports the PathPilot CNC controller, which is user-friendly and suitable for both beginners and experienced users.
- Hardinge Gang Tool Lathe: This model is celebrated for its robust construction and reliability. It typically comes with a 5 HP spindle and options like a 5c collet or 4″ chuck, making it a versatile choice for various machining operations.
- Okuma LC-10: Though it has a unique layout, the LC-10 is built like a tank and goes relatively cheap on the market. It features an 8-station turret and is known for its durability and ease of use.
When choosing a mini CNC lathe, it is also wise to consider the long-term aspects such as the availability of spare parts, aftersales support, and the potential return on investment. High-quality machines from reputable brands often offer better durability and performance, which can be crucial for maintaining productivity and reducing downtime in your machining projects.
Setting Up Your Mini CNC Lathe
Preparing the Workspace
Before we install the mini CNC lathe, it’s essential to create a suitable workspace. First, clear any clutter and ensure there is enough room for the machine to operate safely and efficiently. Consider factors such as lighting, which is crucial for precise work, and ventilation, which is necessary to keep the area free from harmful dust and fumes. Accessibility for maintenance should also be considered to facilitate easy access to the machine for regular checks and repairs.
Installation and Calibration
Once the workspace is prepared, the next step is to install and calibrate the mini CNC lathe. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure proper installation. This process typically involves attaching the machine to a sturdy workbench or stand, connecting power and data cables, and securing any necessary accessories.
Calibrating the machine is crucial for achieving accurate machining results. This involves adjusting parameters such as tool offsets, spindle speed, and feed rate. For precise calibration, consult the user manual or seek guidance from an experienced technician. Remember, the calibration process includes setting the X offset for each tool by following specific steps like machining a test piece, measuring dimensions, and adjusting settings in the control panel.
Safety Precautions
Operating a mini CNC lathe involves inherent risks, so prioritizing safety is crucial. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety glasses, gloves, and ear protection. Familiarize yourself with the emergency stop buttons and other safety features of your specific machine. Keep the work area clean and free from obstructions that may interfere with machine operation. Never leave the machine unattended while it is running. Regularly inspect tools, fixtures, and workpieces for damage or wear that may compromise safety. Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures when performing maintenance or repairs on the machine.
By adhering to these guidelines, we can ensure a safe and efficient setup for our mini CNC lathe, paving the way for successful machining projects.
Familiarizing Yourself with the Control Panel
Once you have successfully set up your mini CNC lathe, it’s crucial to become acquainted with the control panel. This is where all your commands are inputted and adjustments are made to ensure precise machining. The control panel typically includes a screen, various buttons, and knobs, each with specific functions.
Screen Display
The screen on the control panel displays vital information such as tool paths, cutting speeds, and feeds. By understanding how to interpret this data, you can effectively monitor and manage the machining process. It’s essential to get comfortable with reading and interpreting these displays as they provide real-time feedback on your operations.
Buttons and Navigation
The buttons on the control panel allow you to navigate through different menus and select functions necessary for your machining tasks. Familiarity with these buttons is key to efficiently operating your mini CNC lathe. Each button usually has a clear label, but it’s good practice to refer to your manual to understand the specific functionalities and associated commands.
Knobs for Adjustments
Some control panels include knobs that enable you to manually adjust parameters such as spindle speed and tool offsets. These adjustments are crucial for achieving the desired accuracy and quality in your machining projects. Spend time experimenting with these controls to see how they affect the machining process, which will help you better understand how to achieve optimal results.
Advanced Control Features
Operators use modes like handle and jog to move the turret or machine spindle incrementally or steadily, which is essential for precise positioning. The MDI mode allows for the execution of isolated lines of programming, and the memory mode is used to select and edit existing programs. Understanding these modes and when to use them will greatly enhance your ability to use the mini CNC lathe effectively.
Before running a full program, you might choose to execute in single block mode to test the program safely. Additionally, features like optional stop or block delete functions provide further control during the operation, allowing for pauses or edits before proceeding with the full machining process.
Running and Adjusting Programs
The cycle start button on the control panel initiates the programmed operations. Once the program is running, you can use the control interface to adjust cutting variables such as speed and feed with overrides. This capability to make adjustments on the fly is crucial for managing long operations or when working with different materials.
By taking the time to thoroughly understand each aspect of your mini CNC lathe’s control panel, you’ll be better equipped to perform precise and efficient machining tasks. This familiarity not only enhances your workflow but also ensures you can leverage the full capabilities of your equipment.
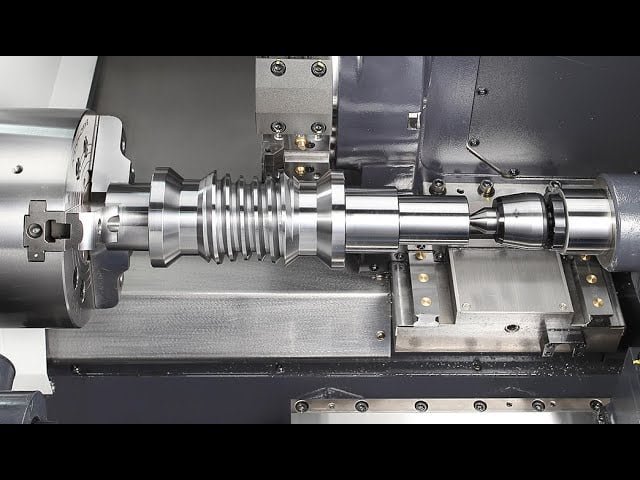
Loading and Securing the Workpiece
Before initiating any machining operation on your mini CNC lathe, it’s crucial to properly load and secure the workpiece. This step ensures stability and precision during the machining process, preventing any movement that could lead to errors or accidents.
- Opening the Chuck Jaws To begin, open the chuck jaws by rotating them counterclockwise. This can be done manually using a chuck key or by an automatic jaw-opening mechanism, depending on your mini CNC lathe model.
- Placing the Workpiece Carefully place your workpiece between the open jaws. Ensure that it is centered to avoid any imbalance or misalignment during the machining process.
- Tightening the Chuck Jaws Secure the workpiece by rotating the chuck jaws clockwise. It is important to tighten the jaws adequately to ensure the workpiece is firmly gripped. However, avoid overtightening as it can damage both the chuck jaws and the workpiece.
- Checking for Stability Once the workpiece is clamped, give it a gentle wiggle to check for any movement. A properly secured workpiece should not wobble or shift. If any movement is detected, re-adjust the tightness of the chuck jaws.
- Setting Part Zero and Tool Length Offsets Before starting the lathe, ensure that your part zero and tool length offsets are correctly set. This step is critical as it prevents the cutting tools from colliding with the workpiece, potentially causing damage to both the tool and the workpiece.
- Using Additional Clamping Methods In some cases, additional clamping methods may be necessary to secure the workpiece adequately. This might include using clamps or fixtures that hold the workpiece securely in place and minimize vibrations. For more complex or irregularly shaped workpieces, consider using custom fixtures or jigs that provide enhanced stability.
By meticulously following these steps, we can guarantee that the workpiece is loaded and secured correctly on the mini CNC lathe, setting the stage for precise and efficient machining operations.
Programming the Mini CNC Lathe
Programming is a vital aspect of operating a mini CNC lathe for precision machining tasks. It involves creating a set of instructions that guide the machine on how to cut and shape the workpiece accurately. To achieve this, several steps and considerations are involved, from choosing the right software to adjusting machine parameters for optimal performance.
Software Options
To program the mini CNC lathe, you can utilize various software options, including CAD/CAM programs or dedicated CNC programming software. These programs enable you to create tool paths, specify cutting parameters, and generate G-code instructions that the machine can interpret. Beginners might start with free software options, which are user-friendly and sufficient for basic projects. As your skills advance, you might consider paid software that offers more features and capabilities. Connecting your computer to the CNC machine typically involves a USB cable with a ferrite collar to reduce signal interference.
Creating G-Code
G-code programming is essential for setting the machine paths, specifying where to move, at what speed, and in what sequence. This code governs tasks that require high precision, such as drilling or intricate part cutting. Common commands in G-code include:
- G01 for linear movement
- G02 and G03 for circular interpolation
- M03 to start the spindle clockwise
- M08 to activate the coolant, and M09 to deactivate it.
Creating effective G-code also involves specifying tool changes with (T), setting the feed rate (F), and controlling the spindle speed (S). Coordinates (X, Y, Z) ensure that the tool is machining the correct part of the workpiece. It’s crucial to save the G-code correctly to avoid errors during the machining process.
Adjusting Parameters for Precision
When programming, factors such as tool selection, cutting speeds and feeds, and the desired dimensions of the finished part must be considered. Adjusting these parameters carefully in the programming software helps achieve precise machining results. For instance, selecting the minimum value of linear displacement determined by the pulse equivalent is critical to minimize rounding errors and enhance machining accuracy.
Advanced simulation tools can be utilized to preview machine operations, which helps in identifying and correcting synchronization issues before actual production begins. Regular training and updates on CNC software and programming techniques are beneficial for maintaining accuracy and preventing code errors. Additionally, routine calibration of the machine ensures that it operates within precise specifications, thereby maintaining product quality.
By understanding and implementing these detailed steps in programming your mini CNC lathe, you can ensure high-quality, precise machining that meets your project requirements.
Advanced Machining Techniques
Exploring Tooling Options One of the significant benefits of utilizing a mini CNC lathe is the versatility it offers through various tooling options. You can choose from a range of tools such as carbide inserts and high-speed steel tools, each designed to handle different materials and machining tasks. By experimenting with these options, you can fine-tune your cutting speeds, feeds, and depths of cut to optimize the machining process for different materials. This flexibility is invaluable for both simple turning operations and more complex tasks like threading or grooving.
Mastering Complex Operations A mini CNC lathe is not limited to straightforward machining tasks. With the right skills and understanding of advanced programming techniques, such as multi-axis machining and contouring, you can unlock the full potential of your machine. These capabilities allow you to create intricate designs and precise threads on cylindrical parts, tasks that would be challenging and time-consuming to perform manually. By mastering these complex operations, the mini CNC lathe becomes a powerful tool for crafting detailed and intricate components.
Achieving High-Quality Finishes Achieving excellent surface finishes is a hallmark of quality machining, and the mini CNC lathe excels in this area. Proper cutting parameters and finishing techniques, such as light cuts or spring passes, enable you to produce smooth surfaces that require minimal post-processing. Advanced features of certain models, like the SYIL L2 CNC Lathe, include vibration damping and rigid construction, which contribute to the superior surface finish quality. The precise control system of these lathes ensures consistent results across multiple workpieces, enhancing productivity by reducing the need for rework.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Common Issues and Solutions
Even the best CNC machines can encounter issues over time. One common problem is the motor failing to run or only running at full speed. If you encounter this, start by checking the power supply and fuse, ensuring they are in good condition. Additionally, inspect the motor brushes and connections for wear or damage. If the motor runs only at full speed, it may indicate a failure of the MOSFETs on the speed control board, which would require replacement.
Another frequent issue is overheating or irregular motor running, often caused by dust build-up or improper lubrication. Regular cleaning and ensuring all moving parts are well-lubricated can prevent these problems. If the issue persists, check for worn or damaged parts like bearings and replace them as necessary.
For more specific component tests, such as checking the fuse holder or testing emergency stop switches, it’s advisable to use a volt/ohm/milliampmeter. This will help you diagnose and resolve the issues accurately.
Regular Maintenance Cloud
To maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your CNC lathe, establishing a regular maintenance schedule is crucial. This includes daily visual inspections for signs of wear, fluid leaks, or loose cables. Proper lubrication according to manufacturer recommendations should be adhered to, preventing premature wear.
It’s also essential to keep the workspace and machine clean, removing metal chips, dust, and other residues that can affect the machine’s function. Regular calibration of tools and ensuring all components are tightly secured will help maintain machining accuracy and prevent vibrations that could lead to damage.
Temperature control within the workshop should be monitored, as extreme fluctuations can affect machine accuracy. Additionally, backing up data and programs regularly protects against potential technical failures.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Machine
Proactive maintenance is key to prolonging the life of your CNC equipment. This includes frequent checks for tool wear and ensuring cutting tools are kept in good condition, which prevents damage to both the workpiece and the machine. Implementing vibration and wear assessments can also help detect issues before they escalate into costly repairs.
Training for system operators is vital, covering proper handling, installation, and maintenance of cutting tools. This not only minimizes downtime but also ensures high-quality production levels are maintained.
By following these maintenance tips and addressing issues promptly, you can ensure the efficiency and reliability of your CNC lathe, ultimately leading to consistent production of high-quality parts and a long-lasting machine.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have embarked on a detailed journey exploring the mini CNC lathe machine, a compact yet powerful tool essential for precision machining. From selecting the appropriate machine for specific needs, setting it up correctly, understanding its control panel for efficient operation, to the programming that drives its functionality and the advanced techniques that unlock its full potential, every aspect has been covered to equip beginners and even seasoned machiners with the knowledge to excel in their crafting endeavors. The importance of troubleshooting and regular maintenance to ensure the longevity and consistent performance of the machine has also been emphasized, highlighting the intricate balance between technical skills and meticulous care required in the world of CNC machining.
As we reflect on the insights shared, it’s evident that the mini CNC lathe machine stands not just as a tool, but as a gateway to innovation in the small-scale manufacturing and personal project spaces. The blend of technology, precision, and creativity it offers promises a broad spectrum of possibilities, ready to be explored by anyone willing to dive into the realm of CNC machining. Embracing the challenges and opportunities presented by this versatile equipment can lead to unparalleled satisfaction in craftsmanship, urging us to continually push the boundaries of what we can create. Let this guide be your stepping stone into the world of precise, efficient fabrication, and may your projects reflect the depth of your learning and the breadth of your imagination.
FAQs
1. How do CNC lathes differ from CNC turning machines?
CNC lathes and turning machines are similar, yet they serve slightly different purposes. While a CNC lathe primarily focuses on turning operations, a CNC turning center encompasses a broader range of capabilities including facing, threading, knurling, drilling, boring, reaming, and taper turning, making it more advanced and versatile.
2. What are some common operations performed on a CNC lathe?
A CNC lathe can perform a variety of operations. The most common ones include turning, facing, grooving, parting, threading, drilling, boring, knurling, and tapping.
3. What distinguishes a CNC lathe from a manual lathe?
The primary difference between a CNC lathe and a manual lathe lies in their operation and functionality. A CNC lathe automates operations through programming and does not require manual gear arrangements to create threads or other complex features. Conversely, a manual lathe requires manual adjustments such as setting the auxiliary tool carriage to specific angles for taper cutting, which must be reset for each new angle or operation.
4. How do lathe machines compare to turning machines in terms of usage?
Lathe machines are typically more suited for short production runs, quick repairs, and simpler parts like pins and bushings, due to their ease of setup and operation. Turning machines, or turning centers, on the other hand, are better suited for larger scale productions due to their enhanced efficiency and broader production capabilities.





Leave a Comment